Understanding the Implications of Loan Default: Causes, Consequences, and Solutions
29
0
Guide or Summary:Loan Default refers to the failure to meet the legal obligations or conditions of a loan, often when a borrower does not make the scheduled……
Guide or Summary:
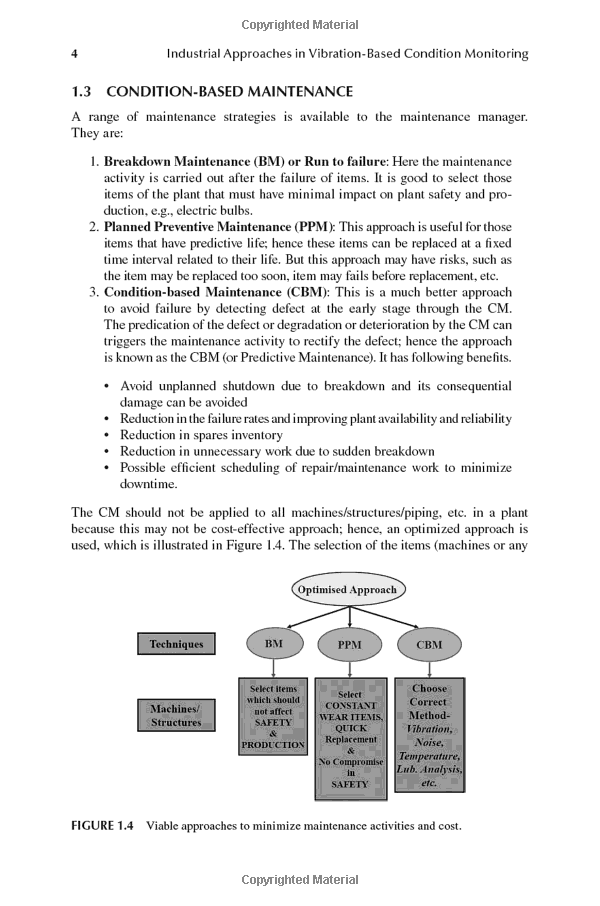
- Loan Default refers to the failure to meet the legal obligations or conditions of a loan, often when a borrower does not make the scheduled payments. This situation can arise from various factors, including financial hardship, unemployment, or poor financial management. Understanding loan default is crucial for both borrowers and lenders, as it can have significant repercussions on credit scores, future borrowing ability, and overall financial health.
- Causes of Loan Default can be multifaceted. One of the most common reasons is unexpected financial difficulties, such as job loss or medical emergencies. Borrowers may also struggle with loan default due to rising living costs that outpace their income, leading to an inability to make timely payments. Additionally, some borrowers take on more debt than they can manage, often due to a lack of understanding of their financial situation or the terms of the loan. Poor financial planning and budgeting can exacerbate these issues, making it difficult to stay on top of payments.
- Consequences of Loan Default are severe and can affect a borrower’s financial future for years. The most immediate consequence is a negative impact on the borrower’s credit score, which can drop significantly after a default. This reduction in credit score can make it challenging to secure future loans or credit, as lenders view defaulted loans as a sign of high risk. Additionally, borrowers may face legal actions from lenders, leading to wage garnishments or liens on their property. In some cases, defaulting on a loan can lead to bankruptcy, which has long-term implications for financial stability.
- Solutions to Avoid Loan Default involve proactive financial management and communication with lenders. Borrowers should create a budget that accounts for all income and expenses, ensuring they can meet their loan obligations. If financial difficulties arise, it is essential to communicate with the lender as soon as possible. Many lenders offer options such as loan modifications, deferments, or repayment plans that can provide temporary relief. Seeking financial counseling or assistance from non-profit organizations can also help borrowers navigate their financial challenges and develop a plan to avoid default.
Loan Default refers to the failure to meet the legal obligations or conditions of a loan, often when a borrower does not make the scheduled payments. This situation can arise from various factors, including financial hardship, unemployment, or poor financial management. Understanding loan default is crucial for both borrowers and lenders, as it can have significant repercussions on credit scores, future borrowing ability, and overall financial health.
Causes of Loan Default can be multifaceted. One of the most common reasons is unexpected financial difficulties, such as job loss or medical emergencies. Borrowers may also struggle with loan default due to rising living costs that outpace their income, leading to an inability to make timely payments. Additionally, some borrowers take on more debt than they can manage, often due to a lack of understanding of their financial situation or the terms of the loan. Poor financial planning and budgeting can exacerbate these issues, making it difficult to stay on top of payments.
Consequences of Loan Default are severe and can affect a borrower’s financial future for years. The most immediate consequence is a negative impact on the borrower’s credit score, which can drop significantly after a default. This reduction in credit score can make it challenging to secure future loans or credit, as lenders view defaulted loans as a sign of high risk. Additionally, borrowers may face legal actions from lenders, leading to wage garnishments or liens on their property. In some cases, defaulting on a loan can lead to bankruptcy, which has long-term implications for financial stability.
Solutions to Avoid Loan Default involve proactive financial management and communication with lenders. Borrowers should create a budget that accounts for all income and expenses, ensuring they can meet their loan obligations. If financial difficulties arise, it is essential to communicate with the lender as soon as possible. Many lenders offer options such as loan modifications, deferments, or repayment plans that can provide temporary relief. Seeking financial counseling or assistance from non-profit organizations can also help borrowers navigate their financial challenges and develop a plan to avoid default.
In conclusion, loan default is a significant issue that can have lasting effects on a borrower’s financial health. By understanding the causes, consequences, and potential solutions, borrowers can take steps to prevent default and maintain their financial stability. It is essential to approach borrowing with caution and to seek help when needed, ensuring that loans enhance financial well-being rather than detract from it.
